However in a covalent bond the atoms are bound to share electrons. See answer 1 Best Answer.
Polar And Non Polar Molecules Vce Chemistry
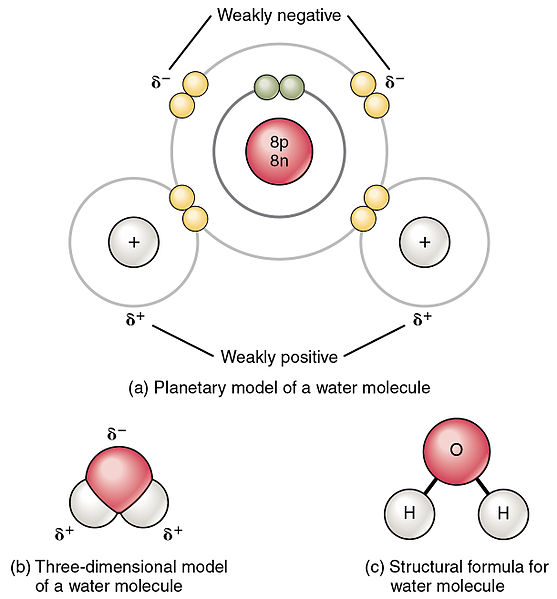
The electronegativity value for oxygen is 344 whereas the electronegativity value for hydrogen is 220.

. It is said that water is the universal solvent but this does not mean that it dissolves universally but rather that due to its abundance it is a suitable solvent to dissolve polar substances Helmenstine 2017. When solutes are added to water they may be affected by. The shape means most of the negative charge from the oxygen on side of the molecule and the positive charge of the hydrogen atoms is on the other side of the molecule.
Many covalent compounds are insoluble in water. The electrons are unequally shared with the oxygen atom spending more time with electrons than the hydrogen atoms. This degree of difference may be higher or lower.
A covalent bond is a bond formed by atom sharing. Polar covalent molecules dissolve well in a polar solvent such as water. Polar molecules occur when atoms share electrons unequally in polar covalent bonds.
For example sodium Na and chlorine Cl form an ionic bond to make NaCl table salt. The most familiar example of a polar molecule is water link. However if we want to define it more accurately a polar covalent bond is a bond that exists between two atoms consisting of electrons that are unevenly distributed.
1 A Describe a polar covalent bond and give an example. The electronegative difference between the H and O allows them to be polar because on side there is positive charge and on another side there is negative charge. Examples of polar covalent bonds The water H 2 O is the most classic example of a polar molecule.
In general a polar bond is a certain class of a covalent bond. Examples of Molecules with Polar Covalent Bonds. A polar bond is a covalent bond in which there is a separation of charge between one end and the other in other words in which one end is slightly positive and the other slightly negative.
Water H 2 O is a polar bonded molecule. A water molecule abbreviated as H2O is an example of a polar covalent bond. Water H 2 O is polar because of the bent shape of the molecule.
Water H2O is a molecule having a polar covalent bond. The electrons are unequally shared with the oxygen atom spending more time with electrons than the hydrogen atoms. In terms of intramolecular bonding there are hydrogen bonds between urea molecules each carbonyl oxygen accepts 4 from N-H hydrogens.
However nonpolar covalent molecules do not dissolve well in waterfor example water and oil. Describe and differentiate between covalent and ionice bonds using examples of each. The hydrogen-chlorine bond in HCl or the hydrogen-oxygen bonds in water are typical.
For example if we talk about water H2O it is a polar covalent bond. Depending on the degree of electronegativity difference the covalent character can be changed. Molecular bonds are another name for covalent bonds.
Describe polar covalent bonds using water as an example. For example when the same atoms are joined to form molecules like Cl 2 H 2 or P 4 each atom is bonded to another by a covalent bond. Covalent Bond Definition Types Properties Examples.
The more electronegative atom is said to have a partial negative charge and the less electronegative atom has a partial positive charge in the polar covalent bond. The inequality in electron distribution accounts for the bent shape of the molecule. The electronegativity value of oxygen is 344 while the electronegativity of hydrogen is 220.
There are two types of covalent bonds. In water molecule there are twice the number of hydrogen atoms than the oxygen atoms. The molecule has three parts.
B Describe a nonpolar covalent bond and give an example. Therefore the bond electron pair is pulled. Describe polar covalent bonds using water as an example.
The electrons are unevenly shared with the oxygen atom using more time with electrons than the hydrogen atoms. Its structure is H-O-H. Water cannot hydrate these molecules.
An illustration describing the polarity of the covalent bonds in a water molecule is provided above. An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond in which the atoms have different electronegativity values from each other. The oxygen side of the molecule has a net negative charge while the two.
In a non-polar covalent bond the sharing of electrons between the atoms is equalThis depends on the difference between the. The difference in the distribution of electrons accounts for the best shape of the molecule. A covalent bond is formed when electrons from both participating atoms are shared equally.
One atom of oxygen the nucleus of which contains eight protons and two hydrogen atoms whose nuclei each contain only one proton. A covalent bond is a bond where atoms share electrons. The water H 2 O is the most classic example of a polar molecule.
We can also say that it is the dividing line between the formation of a pure covalent bond and an ionic bond. A polar covalent bond is formed when atoms which are having different electronegativities and share electrons between them. The sharing of bonding pairs will ensure that.
Examples of molecular compounds that dissolve well in water are sugar and ethanol. Examples of polar covalent bonds. Since electrons spend more time with the oxygen atom it carries a partial negative chargeAnother example of a polar covalent bond is between a.
In a polar covalent bond shown in Figure 1 the electrons are unequally shared by the atoms and are attracted more to one nucleus than the otherBecause of the unequal distribution of electrons between the atoms of different elements a slightly positive δ or slightly negative δ. Examples include most covalent bonds. For water the.
This is an example of polar covalent chemical bonding. A water molecule condensed as H2O is an example of a polar covalent bond. The CO bond is a double covalent bond while the C-N bonds are single covalent bonds.
Since electrons consume more time with the oxygen atom it carries a partial negative charge. The pair of electrons involved in this type of bonding is known as a shared pair or bonding pair. Difference Between Covalent and Ionic Bonds.
A water molecule abbreviated as H2O is an example of a polar covalent bond. For water the structure is H-O-H. The oxygen side of the molecule features.
Examples of Molecules with Polar Covalent Bonds.

Polar Covalent Bond Definition And Examples

0 Comments